Explore Trusts in RightCapital
RightCapital enables advisors to capture every element of a client's financial landscape, including common trust strategies. This article provides an overview of trust types and how they can be used strategically within RightCapital.
To review how existing trust-owned properties, investments, and insurance policies are incorporated into a financial plan, please review this article.
Trusts Overview
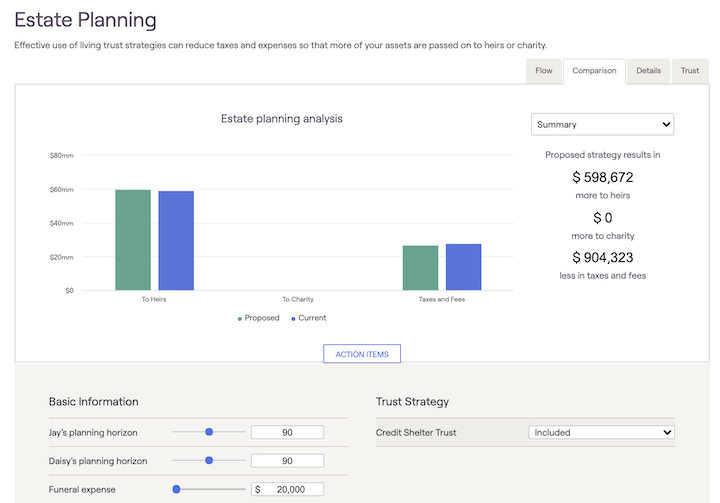
RightCapital allows advisors to quickly demonstrate the benefits of trust strategies to clients within their financial plans. To illustrate the value of specific trust strategies, advisors can use the Estate > Analysis planning module. This module allows advisors to compare trust strategies against the current planning scenario in the following ways:
How much more money can go to the heirs
How much more money can go to charity
How much less can the client pay in taxes
The impact of trust distributions on retirement income
Trust Types In RightCapital
Revocable Trust
RightCapital allows Revocable trusts to be entered as the owner of specific accounts in the Profile > Net Worth area. Revocable Trusts will not be an available trust strategy within the Estate > Analysis.
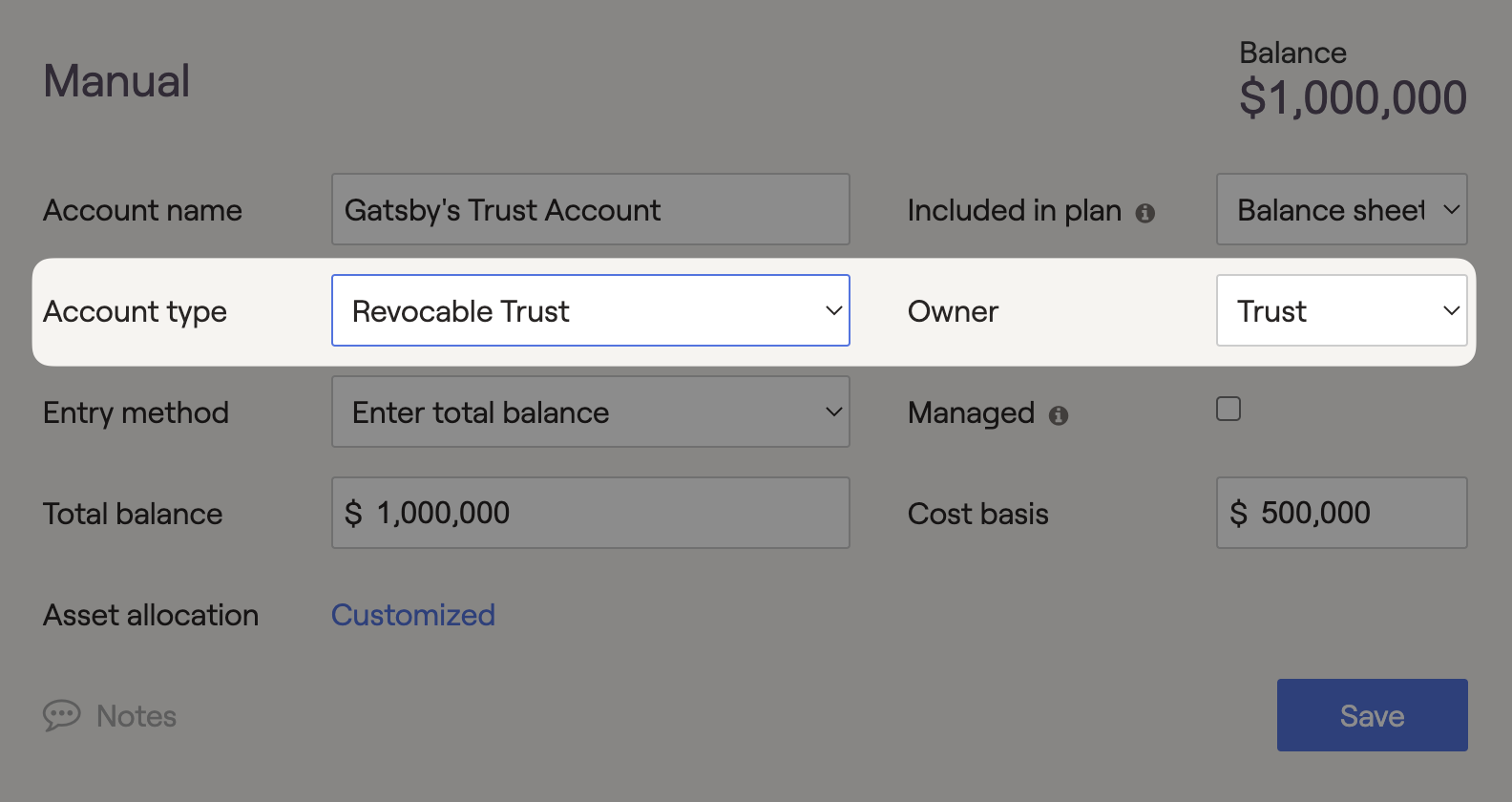
Revocable trusts are typically used within an estate planning strategy to manage and protect assets. In Revocable trusts, the grantor can revoke or amend the trust until they pass away. After the grantor passes away, the trust becomes irrevocable. Revocable trusts allow beneficiaries to avoid probate court but do not shelter assets from the estate or income tax.
Once revocable trusts are assigned as the owner of an account, the assets will be listed in the ‘Trust’ column on the client's Balance Sheet. These accounts will be included in the taxable investments and can be used to fund cash flow deficits. The percentage of taxable investments associated with a Revocable trust will be excluded from probate costs in the Estate > Analysis module.
Credit Shelter Trust (CST)
In RightCapital, Credit Shelter Trusts can be assigned as the owner of any investment account. Users can also indicate any income distributed from the CST's to fund cash flow needs. CST's can be used as a proposed trust strategy within the Estate > Analysis module.
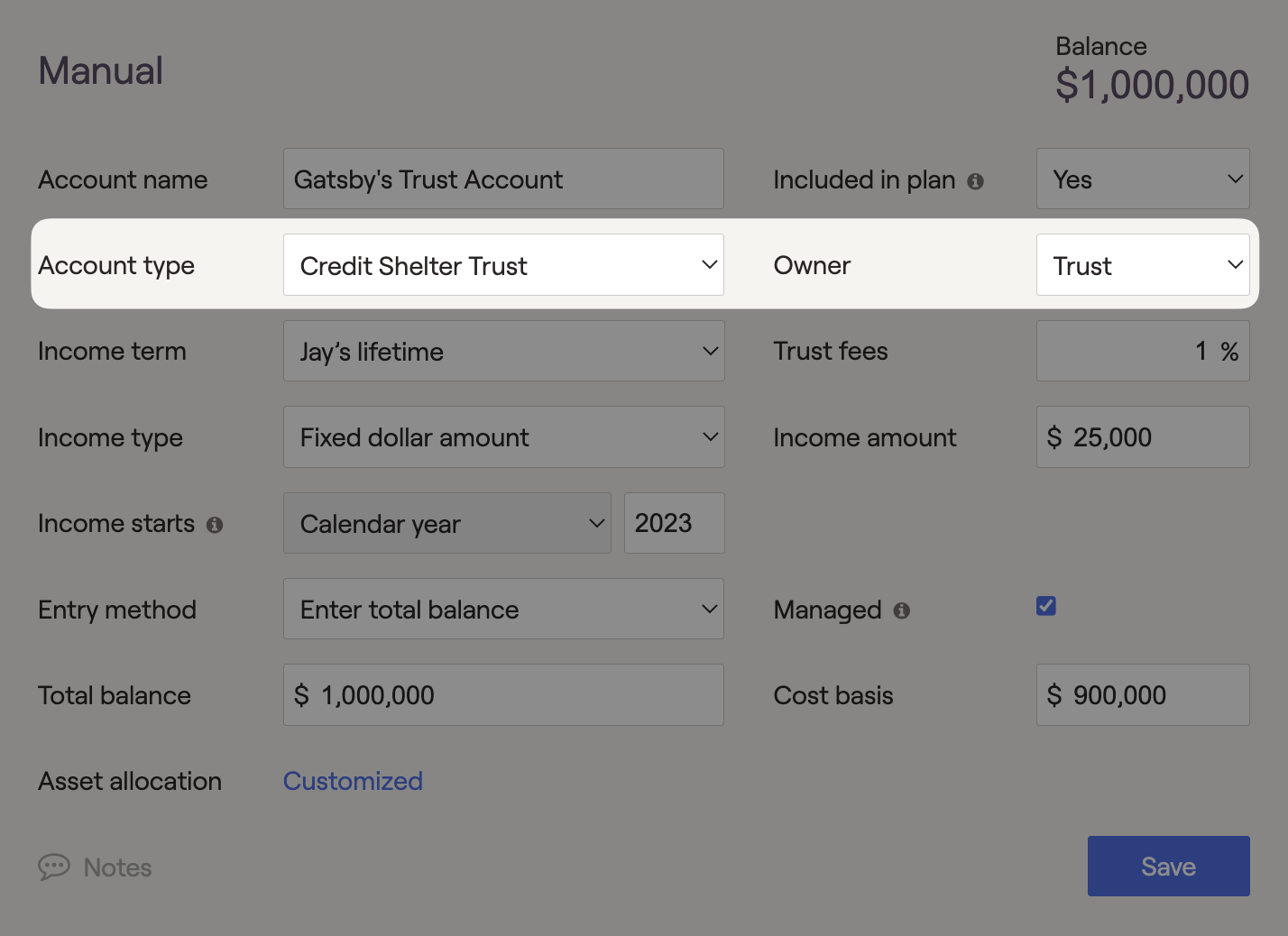
Once Credit Shelter Trusts are entered into the Net Worth, they will be listed in the trust column on the client's Balance Sheet. Assets in the CST are held outside the estate and will reduce federal estate taxes when applicable. After the surviving spouse's death, assets held within the CST are transferred to the beneficiaries without federal or state estate taxes. The federal estate tax applies when an individual's assets exceed $15,000,000 (2026) in today's dollars upon passing away. Placing assets into a CST within RightCapital's Estate module can reduce assets below the estate tax exemption threshold, reducing taxation and passing more assets onto the heirs. This trust type can also generate additional income within the financial plan.
Charitable Remainder Trust (CRT)
Charitable Remainder Trusts can be assigned as the owner of any investment account in a financial plan. Charitable Remainder Trusts represent an irrevocable relationship that allows an individual to reduce taxable income by donating assets to charity. Assets placed in a CRT produce income for the beneficiary over some time before the remainder is donated to charity. CRTs can be used as a proposed trust strategy within the Estate > Analysis module.
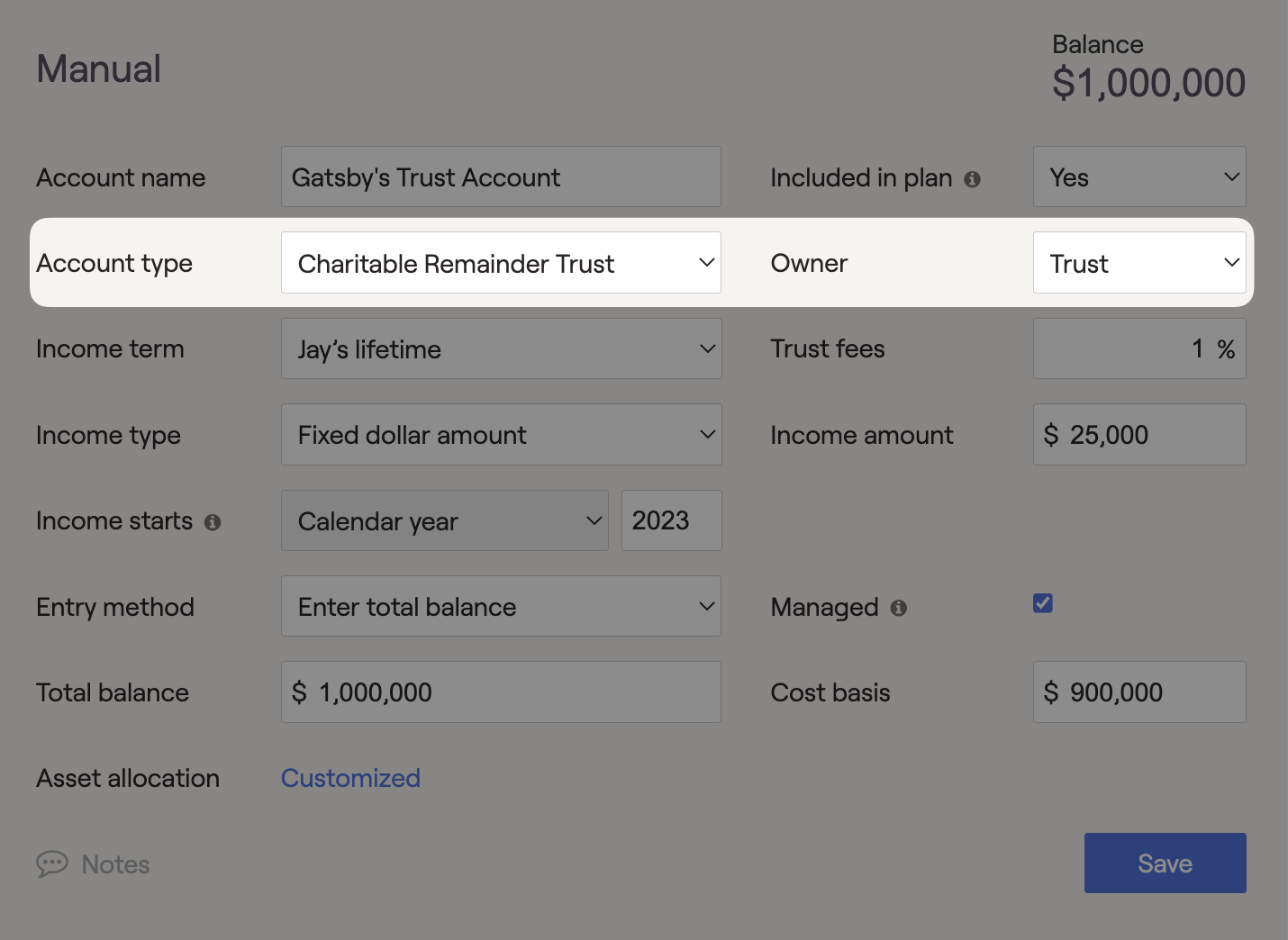
Once CRTs are entered into the Net Worth, they will be listed in the trust column on the client's Balance Sheet. This trust type can generate additional income within the financial plan to fund cash flow needs. Proposing a CRT in the Estate > Analysis > Action Items allows the grantor to hold assets in the CRT outside the taxable estate, reducing or eliminating the federal estate tax. Tax deductions associated with setting up a CRT must be calculated outside RightCapital and added to the Estate > Analysis Area.
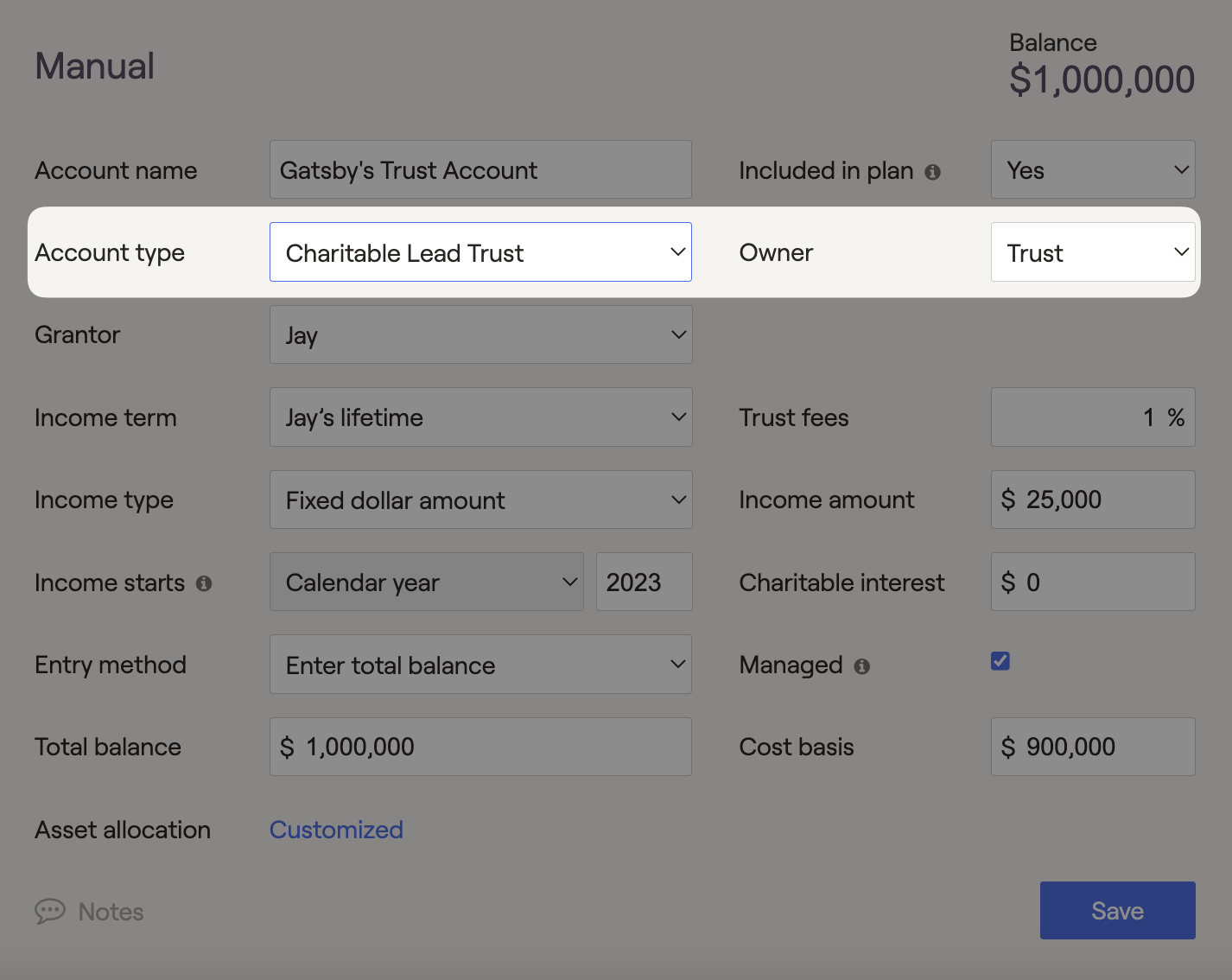
Charitable Leads Trust (CLT's)
Once the Charitable Leads Trust is assigned as the owner of an investment account, it offers income distributions to a charity before being allocated to non-charitable beneficiaries. This trust type can be viewed as a grantor or non-grantor trust by changing the Grantor field from client to none.
Irrevocable Life Insurance Trust (ILIT)
In RightCapital, any term, whole, or universal life insurance policy can be listed with an ILIT as the owner. Placing life insurance policies into an ILIT allows the grantor to remove the life insurance death benefit amount from their taxable estate. This trust can help beneficiaries cover costs and control how the death benefit is distributed. ILITs can be a proposed trust strategy within the Estate > Analysis module.
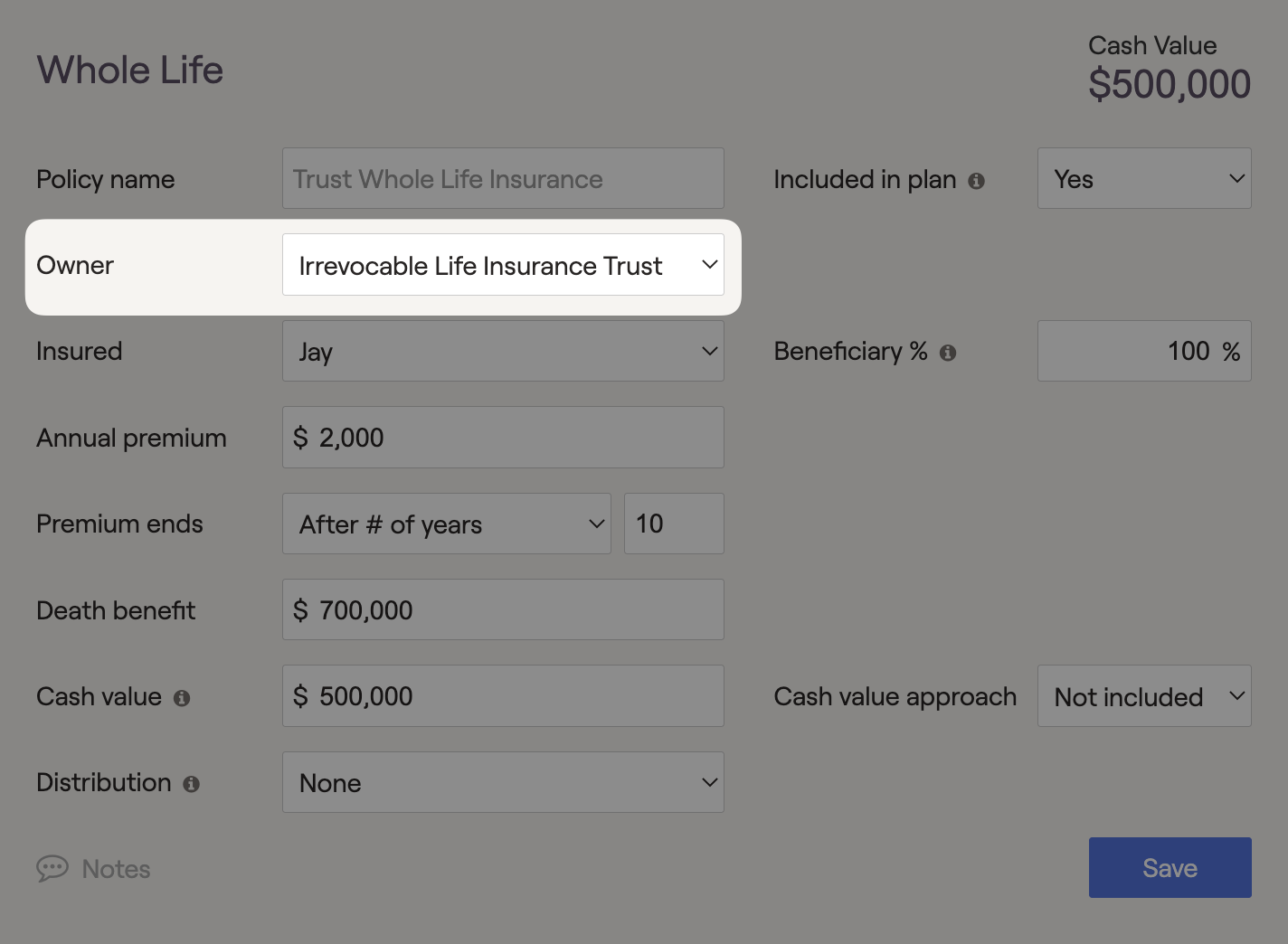
Placing a life insurance policy into an ILIT will remove the death benefit from the client's taxable estate and reduce the impact of federal estate taxes when applicable. The federal estate tax applies when an individual's assets exceed $15,000,000 (2026), in today's dollars, upon passing away. Placing assets into an ILIT within RightCapital's Estate module can reduce taxation and pass more assets onto the heirs. ILIT's can also be established to cover funeral, probate, and estate taxes at the end of a client's life.
Spousal Lifetime Access Trust (SLAT)
SLAT's are irrevocable trusts that allow for the transfer of assets from one spouse to another. This allows the grantor to designate income to the spouse and choose beneficiaries after they pass away. For federal tax purposes, a SLAT is treated as a Grantor Trust, where the Grantor is responsible for taxes on income generated by the trust.
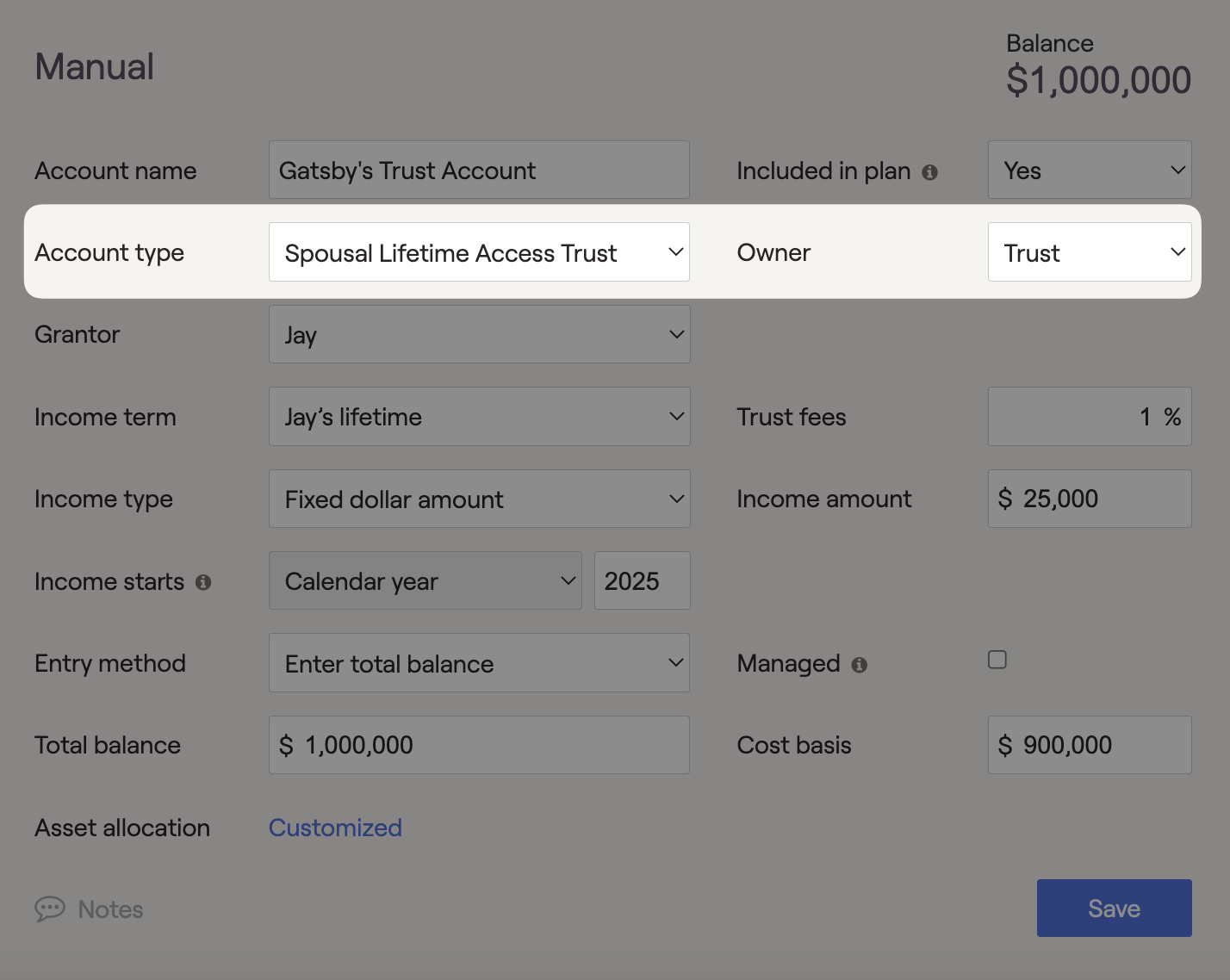
In RightCapital, SLAT's can generate income within the financial plan. Additionally, placing invested assets into a SLAT will remove them from the client's taxable estate and reduce the impact of federal estate taxes when applicable. The federal estate tax applies when an individual's assets exceed $15,000,000 (2026), in today's dollars, upon passing away.
Qualified Terminable Interest Trust (QTIP)
QTIP's are irrevocable trusts typically funded with a deceased grantor's assets. This allows the assets to pass to a family member tax-free. These trusts can produce income for a surviving spouse while remaining assets are transferred to specific heirs. The trust's assets will be included in the client's taxable estate.
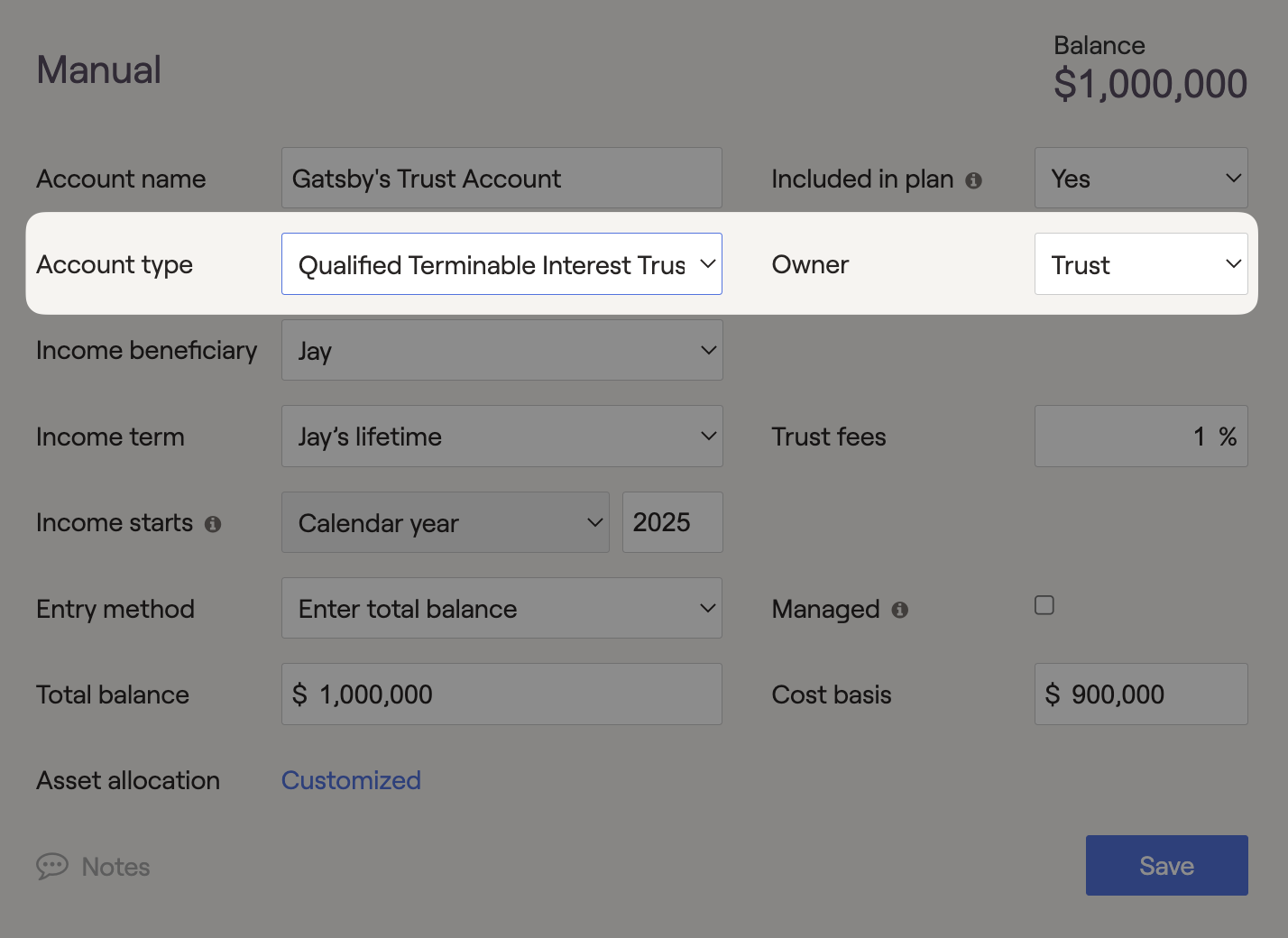
In RightCapital, the income flowing from the QTIP will be automatically calculated as interest plus dividends from the associated investment allocation and not taxed within the plan. This trust can be used to fund cash flow needs in the future. It will also count towards the federal estate tax exemption amount that applies when an individual's assets exceed $15,000,000 (2026), in today's dollars, upon passing away.
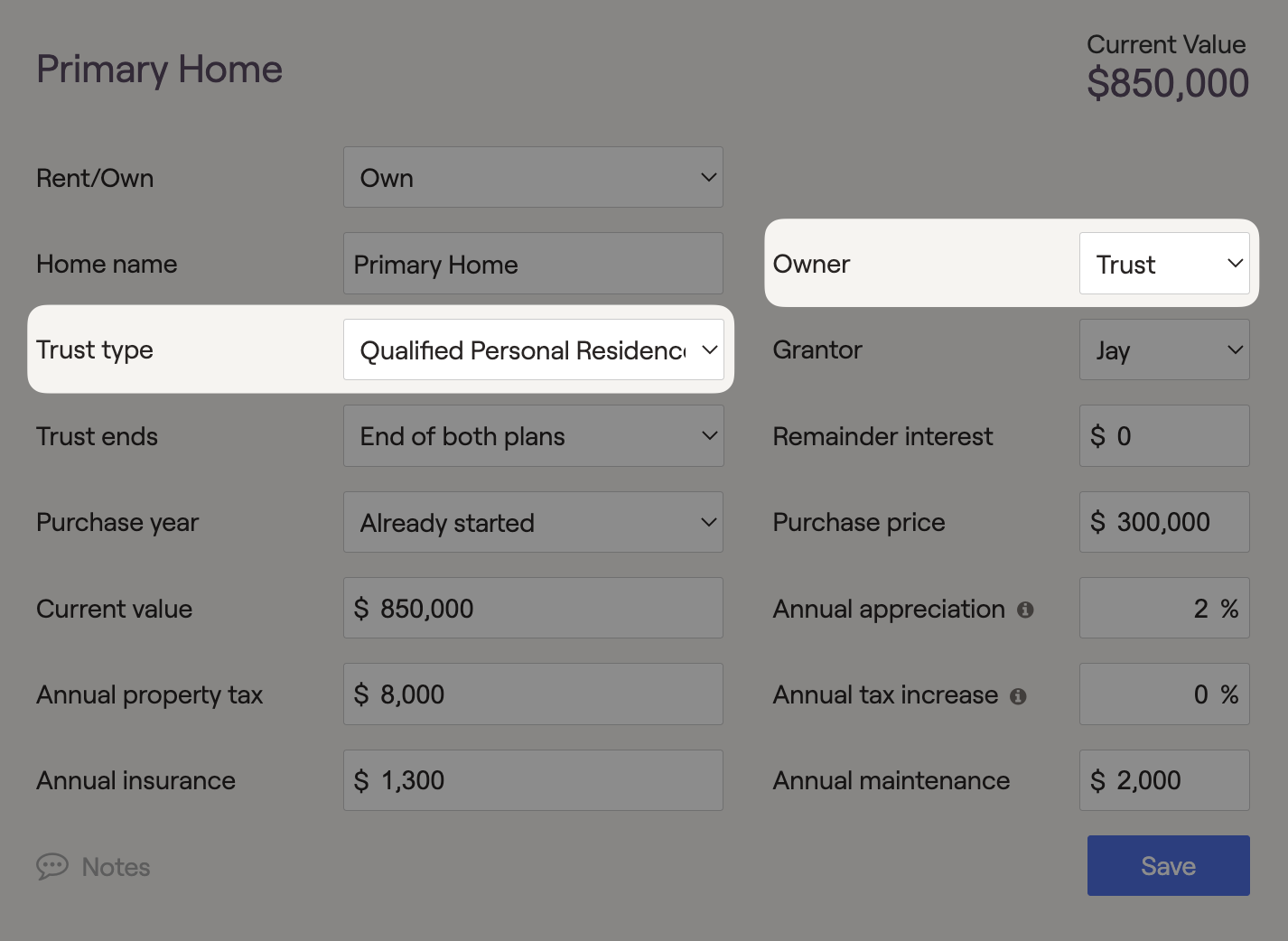
Qualified Personal Residence Trust (QPRT)
QPRT's can be used as the owner of any Primary Home or Vacation Home listed in the client's Profile > Net Worth area. This type of trust is set up to remove future appreciation of a personal residence from the estate. If the grantor dies before the end of the trust, the property value will be re-included in the client's taxable estate.
Grantor Retained Annuity Trust (GRAT)
GRAT's are a type of irrevocable gifting trust that allows individuals to transfer highly appreciating property or assets to a beneficiary with minimal gift or estate tax. The trust also pays out an annuity to the grantor every year, which can work as part of the retirement income strategy. For federal tax purposes, a GRAT is treated as a Grantor Trust, where the Grantor is responsible for taxes on income generated by the trust.
The GRAT provides income to the grantor while the remaining value is passed to beneficiaries without incurring gift taxes. Since the Grantor is responsible for taxes on interest, dividends, and gains generated by the trust, you must indicate details within the "Grantor" dropdown menu. The annuity income stream is not taxed as it enters the client's plan.
If the grantor dies within the trust's GRAT term (Income term), the remaining value is added back into the plan as income. If the client outlives the GRAT, the appreciation assets are passed to beneficiaries tax-free.
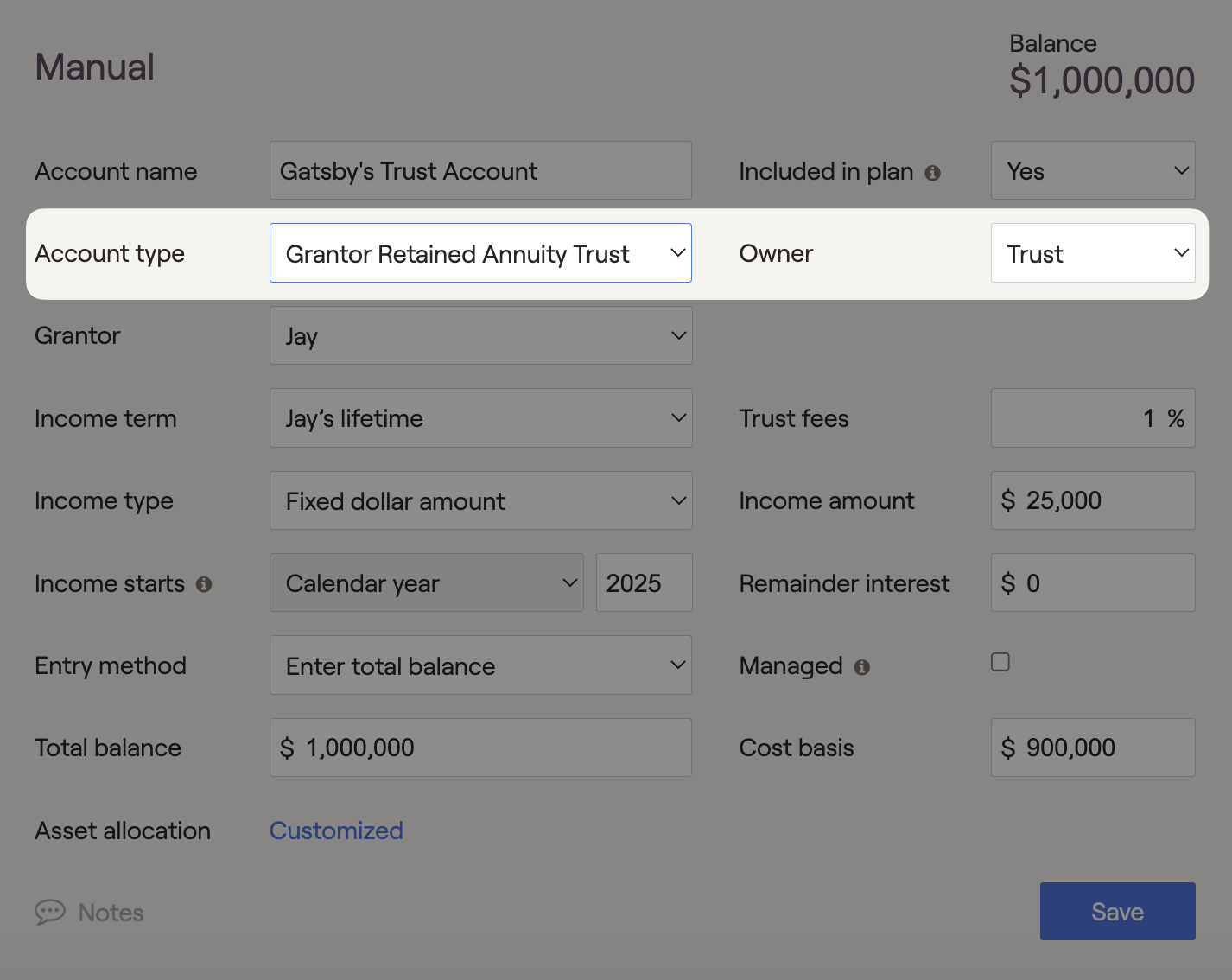
In RightCapital, GRATs can generate tax-free income to fund cash flow needs. Additionally, placing invested assets into a GRAT will remove them from the client's taxable estate and reduce the impact of federal estate taxes when applicable. The federal estate tax applies when an individual's assets exceed $15,000,000 (2026), in today's dollars, upon passing away.
Intentionally Defective Grantor Trust (IDGT)
Once entered into the client's Net Worth, IDGT's provide income to the grantor while the remaining value is passed to beneficiaries without incurring taxes. Since the Grantor is responsible for taxes on interest, dividends, and gains generated by the trust, you must indicate details within the "Grantor" dropdown menu. The annuity income stream is not taxed as it enters the client's plan.
When created, assets are sold to the trust instead of gifted to avoid gift taxes. Therefore, the assets can be sold for a note receivable instead of an income stream annuity. If the grantor dies within the IDGT (Income term), the remaining value is added back into the plan as income. If the client outlives the IDGT, the appreciation assets are passed to beneficiaries tax-free.
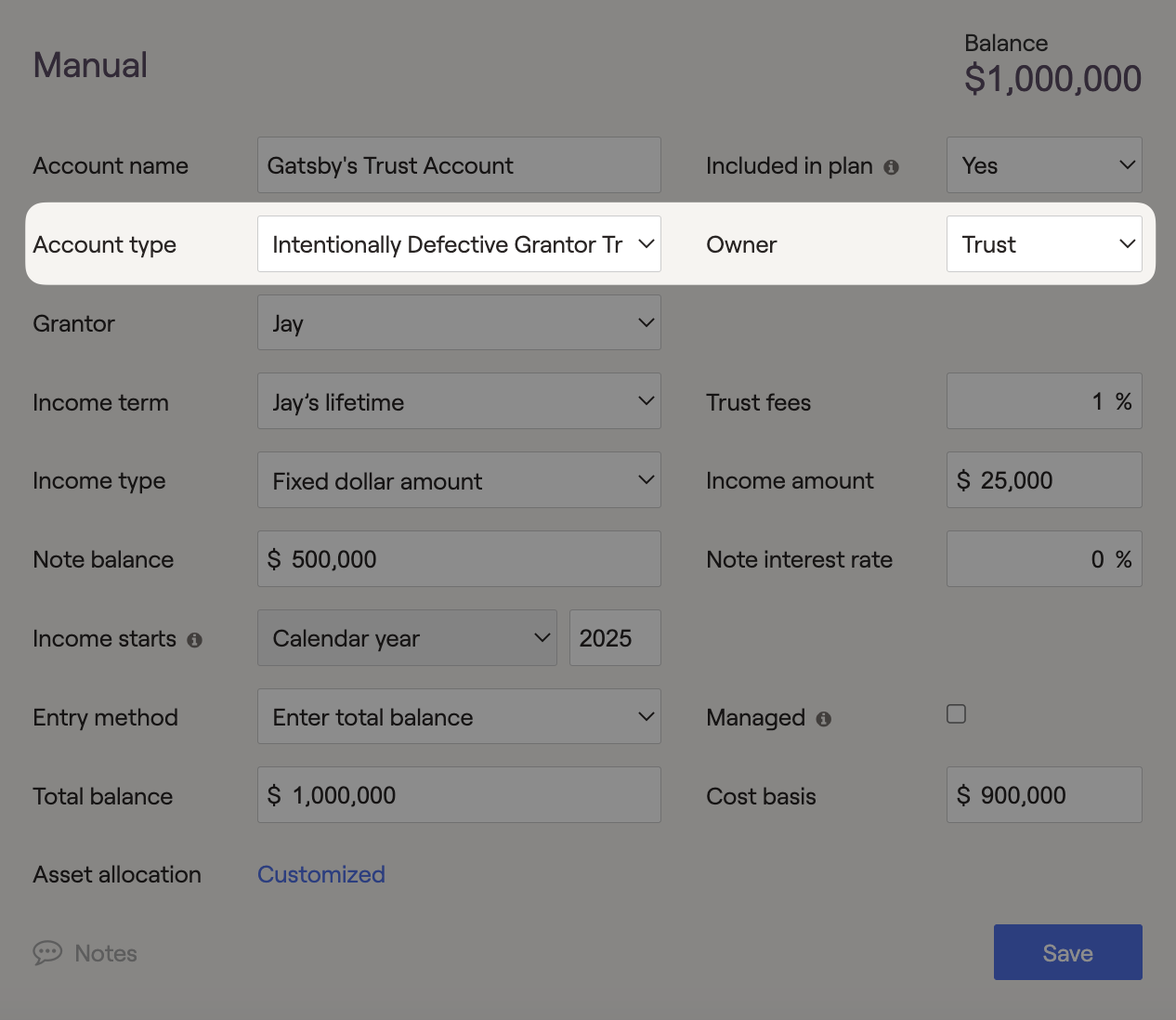
In RightCapital, IDGTs can be used to generate tax-free income to fund cash flow needs. Additionally, placing invested assets into an IDGT will remove them from the client's taxable estate and reduce the impact of federal estate taxes when applicable. The federal estate tax applies when an individual's assets exceed $15,000,000 (2026), in today's dollars, upon passing away.
Irrevocable Grantor Trust
Once the Irrevocable Grantor Trust is entered into the client's net worth, the assets will be placed outside the client's taxable estate. Assets in this trust will not be subject to probate costs or estate taxes in the financial plan. Income can impact the client's cash flows or be sent to individuals outside the plan, using the "% income to heirs field". In a Grantor trust, the client is responsible for any taxes on income generated within the trust's investments. Irrevocable Grantor Trusts can be set as the owner of any property or investment account in RightCapital.
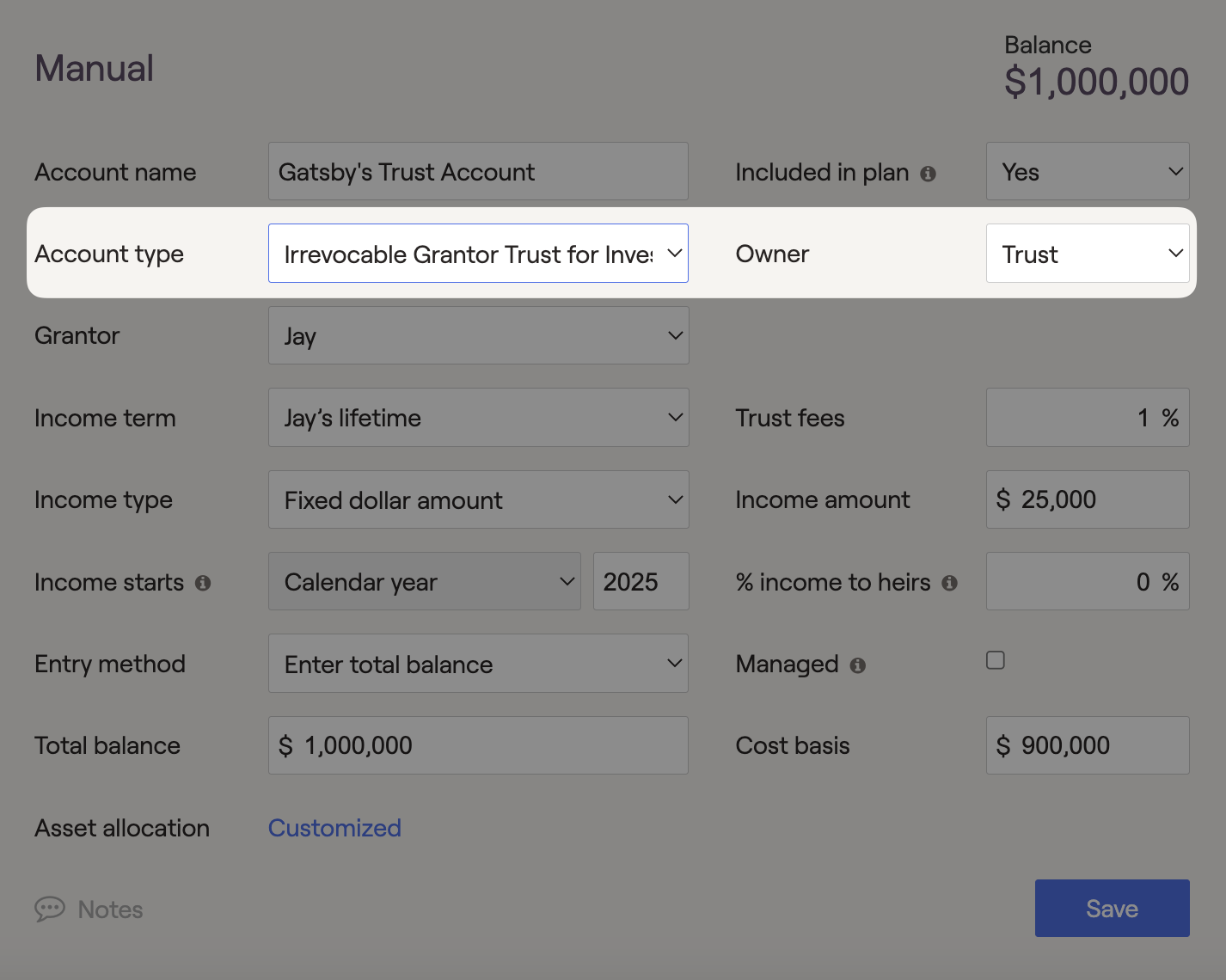
This type of trust can be used to model the essential details of various Irrevocable Grantor Trusts. After being entered into the client's net worth, assets within the Irrevocable Grantor Trust are listed under the trust column of the client's balance sheet. Additionally, placing invested assets into an Irrevocable Grantor Trust will remove them from the client's taxable estate and reduce the impact of federal estate taxes and probate costs when applicable. The federal estate tax applies when an individual's assets exceed $15,000,000 (2026), in today's dollars, upon passing away.
Tax on Trust Distributions
In RightCapital, distributions from the trust's principal balance are not considered taxable, while earned interest, dividends, and capital gains are taxed as personal income tax. The interest, dividend, and capital gains are distributed to the beneficiary first. Only after all the earnings are distributed will the principal balance payout to beneficiaries.
The grantor will receive an immediate tax deduction when establishing a Charitable Remainder Trust. This deduction needs to be calculated outside of RightCapital and added in manually. This can be added as an above-the-line deduction in the profile > Expense > Other expense card, or it can be entered within the Estate > Analysis > Action Items when proposing a CRT strategy. In RightCapital, distributions from the trust's principal balance are not taxable. Distributions from the trust's earned interest, dividends, and capital gains are taxed as personal income tax. The interest is distributed first to the beneficiary within RightCapital, followed by dividends and capital gain. No earnings will be taxed when the trust balance is transferred to charity.
For federal tax purposes, a SLAT is treated as a Grantor Trust, where the Grantor is responsible for taxes on income generated by the trust. Income distributions to the beneficiary will occur tax-free.
QTIPs produce income distributions to the beneficiary that are not taxable within the financial plan.
For federal tax purposes, a GRAT is treated as a Grantor Trust, where the Grantor is responsible for taxes on income generated by the trust. Income distributions to the beneficiary will occur tax-free.
For federal tax purposes, an IDGT is treated as a Grantor Trust, where the Grantor is responsible for taxes on income generated by the trust. Income distributions to the beneficiary will occur tax-free.